It is a centralized administration tool designed to manage and control devices and users that use vMatrix technology.
vMatrix is a desktop virtualization platform developed by the company vCloudPoint. This platform enables the deployment and management of shared virtual desktops on a centralized server, allowing multiple users to access applications and computing resources from thin client devices, such as vCloudPoint Zero Clients.
vMatrix Server Manager provides an intuitive user interface that allows IT administrators to monitor and manage various aspects of the vMatrix infrastructure, such as resource allocation, configuring access policies, installing and updating software, monitoring system performance, and remote troubleshooting.
In short, vMatrix Server Manager is an essential tool for managing and optimizing desktop virtualization environment based on vMatrix technology, ensuring optimal performance and smooth user experience for end users.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is vMatrix Server Manager?
-
What is RDP Wrapper?
It is an open source software application that allows you to enable the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) service on Windows operating systems that do not normally support simultaneous RDP connections. This tool provides an alternative solution to allow multiple users to connect and control a computer remotely through Windows Remote Desktop. RDP Wrapper works by patching system files and modifying system settings to allow additional RDP connections, providing more flexibility and functionality to users who want to access their systems remotely.
-
What are the advantages of using RDP Wrapper?
Enable Simultaneous RDP Connections: RDP Wrapper allows you to enable simultaneous Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connections on Windows systems that do not normally support it, such as Home or Starter editions, allowing multiple users to access and control the same computer remotely .
No Additional Licenses Required: Unlike official Microsoft solutions that require the purchase of additional licenses to enable additional RDP connections, RDP Wrapper provides an alternative solution at no additional cost.
Facilitates Systems Administration: By allowing additional RDP connections, RDP Wrapper can simplify systems administration by allowing multiple users to access and work on the same computer remotely, which can be useful for technical support, collaboration or administration tasks remote.
Flexibility and Scalability: RDP Wrapper offers flexibility and scalability by allowing additional RDP connections to be enabled as needed, without the need for costly license or hardware upgrades.
Wide Compatibility: RDP Wrapper is compatible with a wide variety of Windows operating system versions and editions, making it useful for a variety of usage scenarios and environments.
Customization and Configuration: RDP Wrapper offers advanced configuration options that allow you to customize and adjust the behavior of RDP connections according to the specific needs of the user or organization.
In summary, RDP Wrapper provides a practical and cost-effective solution for enabling additional RDP connections on Windows systems, offering flexibility, scalability, and ease of management for users and organizations that need to access and control their computers remotely. -
What are the disadvantages of using RDP Wrapper?
Despite its usefulness in enabling RDP connections on systems that do not normally support it, using RDP Wrapper can also have some disadvantages:
Limited Compatibility: Although RDP Wrapper can work on many versions of Windows, there may be cases where it is not supported on certain editions or versions of the operating system, limiting its usefulness in some cases.
Potential security issues: When modifying system files and operating system settings, there is a potential security risk when using RDP Wrapper. Patching system files could leave your computer vulnerable to malware attacks or unexpected errors that could compromise system stability.
Windows Updates: Regular operating system updates may interfere with the operation of RDP Wrapper. After a major Windows update, RDP Wrapper may need to be re-patched or tweaked to keep it working properly.
Performance and stability: Depending on the hardware and specific system configuration, the use of RDP Wrapper could affect system performance and stability. Additional RDP connections can increase the load on the system, which could lead to a less smooth user experience or stability issues.
In summary, although RDP Wrapper can be a useful solution in certain cases, it is important to carefully evaluate its advantages and disadvantages before implementing it, especially in enterprise environments or where security and system stability are important priorities. -
What is Microsoft RDS CAL?
CAL is the abbreviation for Microsoft Remote Desktop Services Client Access License. It is a license required to allow users or devices to legally access the advanced features of Remote Desktop Services (RDS) on Windows servers. These features include remote desktop sessions, remote applications, and other desktop virtualization features. Microsoft RDS CALs ensure legal compliance and licensing rights to access and use these features, and are required for each user or device accessing the RDS environment concurrently.
-
What is the similarity and difference between RDP Wrapper and Microsoft RDS CAL?
RDP Wrapper and Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS) CALs (Client Access Licenses) are two related but different concepts in the context of remote connections in Windows environments.
Principal function:
RDP Wrapper: Allows you to enable Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connections on Windows operating systems that do not normally support simultaneous RDP connections, such as Home or Starter editions.
Microsoft RDS CALs: These are licenses required to allow users or devices to access advanced Remote Desktop Services (RDS) features on Windows servers, such as remote desktop sessions, remote applications, and other desktop virtualization features.Purpose:
RDP Wrapper: Its main purpose is to provide an alternative solution to enable additional RDP connections on Windows systems without the need to purchase additional access licenses.
Microsoft RDS CALs: These licenses are required to meet Microsoft licensing requirements and enable access to advanced RDS features on Windows servers.Licensing:
RDP Wrapper: It is not directly linked to Microsoft licensing, as it is a third-party tool that modifies the behavior of the operating system to enable additional RDP connections.
Microsoft RDS CAL: Requires the purchase and assignment of client access licenses for each user or device that accesses Remote Desktop Services features on Windows servers.
In summary, while RDP Wrapper provides a workaround for enabling RDP connections on Windows systems, Microsoft RDS CALs are official licenses required to access and use the advanced features of Remote Desktop Services on Windows servers in a legal and policy-compliant manner. Microsoft licensing. -
Why do Zero Clients disconnect from time to time?
By factory default, Zero Clients and vMatrix Server Manager software are configured for use in an Internet-connected (WAN) environment. If your Main Computer has Internet, no additional configuration is necessary. The operating mode displayed on the user management page of any device that connects to the Main Computer will automatically change from "offline" in red to "online" in black, which means that the device works correctly in an environment provided with Internet.
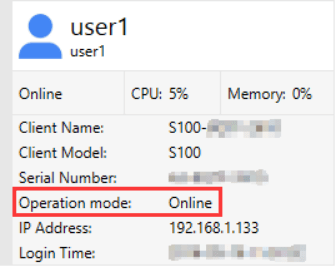
However, if the operating mode of the devices that connect to the Host Computer remains "Offline" in red all the time, you will need to reconfigure the devices for offline use; Otherwise, the devices may disconnect from time to time during operation. Use cases where you may encounter this issue and need to request "Offline Use" typically include the following:
-
How to Reconfigure Devices for Offline Use?
1) In an environment without an Internet connection, vMatrix Server Manager will display a message window for offline usage configuration within 5 minutes after the Host starts up.
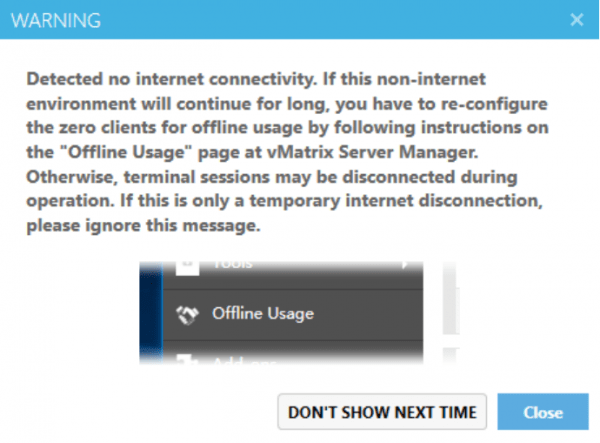
2) Open vMatrix Server Manager, go to the Offline Usage page (this page only appears when the Main Computer does not have an Internet connection during system startup).
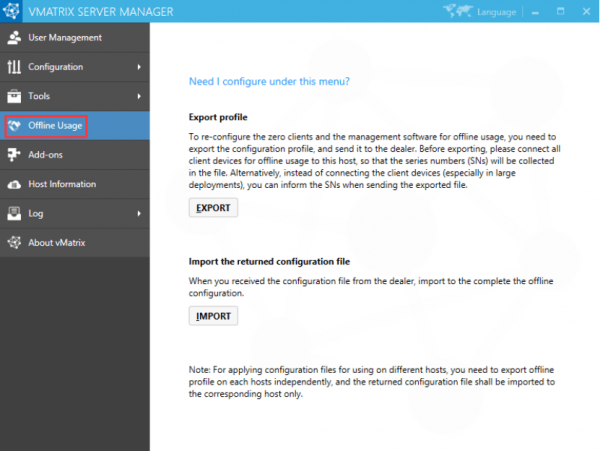
3) Export the configuration profile. Before exporting, connect all Zero Client devices for offline use to the host, so that the serial numbers (SNs) are collected in the file. Alternatively, you can note the SNs if you cannot connect all the Zero Client devices (especially in large deployments). The host profile contains hardware information for the Host Computer. Therefore, please make sure the hardware of the Main Computer, for example, CPU, memory, drives and network card, are exactly the same as their actual offline use condition; Otherwise, if there is any change in the Main Computer hardware, the final generated offline configuration will be invalid. to the host.
4) The reseller will return a configuration file based on your last exported profile. Import the returned file to complete it.
5) If your configuration for offline use is successful, the operation mode changes from "Offline" in red to "Offline" in black.
Note: The offline usage configuration in vMatrix Server Manager was introduced in the release of vMatirx Server Manager version 2.0.2. If you plan to use Zero Clients in a non-internal or unstable Internet environment, use vMatrix Server Manager 2.0.2 or later or contact your reseller to generate an offline configuration file.
Knowledge Base
-
The configuration of a zero client itself does not contribute to its performance
Most customers mistakenly think that a zero client should be, like thin clients, configured high in its internal hardware such as, CPU, flash, network chipset, to gurantee a high performance.
Unlike thin clients that typically use its own client hardware for processing, zero clients push all the computing power to what is running at the host side. In other words, the residing hardware of a zero client do not act on jobs of processing as in PCs or thin clients, but only to initialize a conversation with the network, begin network protocol processes, and display desktop output. Therefore, the configuration of a zero client itself does not contribute to its performance. Even a zero client with powerful configuration as a Pro PC can’t guarantee good performance.
Then what helps with good performance to a zero client?
There are a few aspects:- Well-configured host computer– including sufficient cores and frequency of CPU, IOPS and storage of Disks, size and frequency of Memory. (Multi-threading technology of Intel also helps increasing CPU capability and i series with hardware acceleration performs better than Xeon series of the same level. Disks in RAID configuration increases redundancy and performance. Intensive graphics processing requires sufficient frequency of memory. Video card on the host helps in video playback only.)
- Low latency, high-bandwidth network– recommend local-area network connections provided by standard 100 /1000 Mb/sec networks (i.e. Ethernet) between the host computers and the zero clients.
- High efficient remote display protocol– offers high-resolution sessions, multimedia stream remoting, dynamic object compression, USB redirection, drive mapping and more.
Of the above 3 aspects, only the display protocol is determined by the zero clients. The display protocol determines two critical measures: experience and resource usage. The sticking point for many organizations will be various levels of multimedia support. Regardless of implementation status, any organization can have issues with multimedia support. This is true not only in large implementations that push bandwidth limits — even smaller installations may consume enough bandwidth to push the limits of the display protocol without a bottleneck on the wire. vCloudPoint zero clients utilized our innovative DDP (Dynamic Desktop Protocol) for remote desktop display. This protocol is purpose-built for zero clients and is designed to make efficient use of the network bandwidth and host resources, delivering a user experience that is equivalent to or even better than a business PC. -
Network has a great impact on zero client performance
We all know the zero clients are free of CPU, memory, processor and hardware requirements. This means that another strong factor plays a role in transmitting of the information from server to client. That is the network. And in case of zero clients, this network bandwidth should be really wide and sufficient enough for the seamless transfer of information.
Let us start with an example. S100 zero client uses Ethernet as the network connection. The deployment so far has registered recognition about its appreciable performance, which is attained with the category 5 or 6 network cable to connect to the Ethernet network. The next question is:
What is a Category-5 or Category-6 cable??
Usually, the high quality copper wires are used for Cat-5/ 6 cabling. They are twisted into 4 pairs which run along an outer cover. This design of the cable makes it immune to the other signal interferences, which means a better transmission of the data signal over the cable.
Most of the times, the poor cabling is responsible for the faulty network transmission. This very often leads to the unnecessary testing of the other equipments. There are a few very high standards tagged with the category 5 and 6 cabling, which must be followed during installation as well. This guarantees a high performance over the network.
Recommendation With Us:
For multimedia intensive environments, especially those with concurrent multiple video playback, we recommend a standard 100 /1000 Mbps network between the host computer and the zero clients, to guarantee a smooth high-end experience; as shown in the figures: (click to view large pictures).
The videos consume higher bandwidth, for example, when the server side videos are played at vCloudPoint zero clients, each 480p video file consumes up to 13 Mpbs of the network bandwidth, a 720p video can take up to 15 Mpbs of bandwidth and a 1080p video can take up to 17 Mpbs of bandwidth straight away.
Most of the Wide Area Networks (WAN) have excessive latency and lower bandwidth. This compromises with the rich PC-like experience over the network.
The ideal recommendation from vCloudPoint is a low latency higher bandwidth Local Area Network, which is the secret behind the excellent performance of zero client devices.